Share
Pin
Tweet
Send
Share
Send

Building your own home is not easy. Especially if you are not a professional, do not own complete knowledge, do not wield tools so cleverly. And the first time you build a house. I think there are many such entry-level masters. But do not blame them for mistakes. After all, a passionate desire to create and build simply does not give rest. Then they, like me, have to pass everything through personal experience. So, it happened during the waterproofing of the foundation with my own hands, which I started not at the best moment. However, the situation when the work is easy, fun and fast is considered to be true indicators of the correctness of certain actions. On the other hand, the people already have a saying - go quieter, you will continue. And my story with a couple of vivid photographs will describe a sample of the pen with all the failures and positive aspects.
The meaning of protecting the foundation from moisture
Everything is clear, you say. After all, the meaning of waterproofing the foundation is to protect. The fact is that concrete, no matter how first-class it may be, is designed for a limited number of freezing cycles. Screed's internal moisture content in equal proportion reduces this amount. Because with each freezing, the foundation with internal moisture is destroyed at an accelerated pace. Isolation causes clipping of water sources. The service life is increasing. The second serious nuisance that waterproofing fights is the formation of mold and fungi. Their environment is created by high humidity. Of course, without proper protection.
Nodal moments of cutting water from concrete
During capital construction, methods for waterproofing concrete screed were developed:
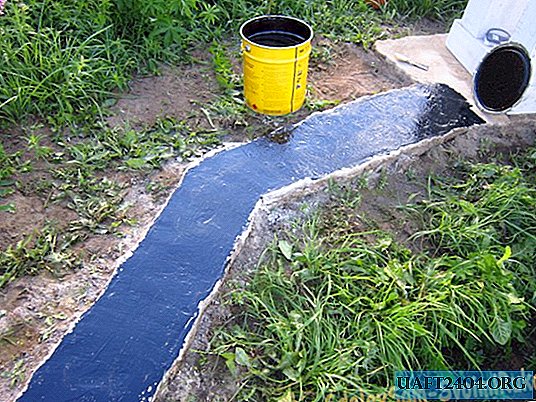
- Laying a trench with roofing material.
- Adding water repellent additives to the cement mortar.
- Processing the visible part of the foundation with spent fuel and lubricants.
- Laying roofing material over the screed.
- The use of bitumen materials.
Looking ahead, I will say that of the above methods, I did not apply all. Although I knew that quality protection works only in combination:
- Fastening sheets of roofing material to the inner side of the formwork and laying it on the bottom of the trench, provide minimal contact with groundwater. Although he is still present. I did not do such manipulations for two reasons:
- At my building site, the primer is deep and the soil is sand.
- The second reason is more trivial. It lies in the desire to save, not buying, as it seemed to me, extra meters of roofing material.
- I used concrete additives in the form of liquid glass. The result was not long in coming. Water repellent properties have appeared.
- Impregnation with used engine oil is used not only for waterproofing, but also for eliminating insects nesting in the pores of concrete. This applies to ants whose colonies on the site are visibly invisible. My neighbor did the processing precisely for this reason. I didn’t do it again. Although the impregnation does create a water-repellent layer that protects from rain.
- I will dwell on the last two points in more detail, since they are the subject of my story. It's about laying roofing material on top of the foundation and the use of bitumen mastic. I did not use bitumen itself. But he acquired a set of two materials working together. This is bituminous mastic and a ruberoid glued onto it over the screed. Protection is fail-safe. But the technology was not without surprises. About them further.
Overview of basic materials for screed waterproofing
What at the time of using the materials I knew about them.
Ruberoid is a roofing cardboard. It is impregnated with oil products. In particular, bitumen. And in two layers:
1. The inner is soft bitumen.
2. External - refractory.
To increase the strength, an external powder is used. The advantages of this product are enough:
- Reliability.
- Durability.
- Compliance in independent execution.
- Provides waterproofing and vapor barrier.
Not without ruberoid deficiencies:
- He is afraid of direct sunlight. Therefore, it requires finishing with plaster. Although not always.
- The material located in the ground is protected with asbestos-cement sheets. Also not always.
- Ruberoid does not tolerate caking. The problem is solved by storage in an upright position.
A few words about the varieties of the product. There are roofing and lining material. They differ in density:
1. Lining has an indicator of 300 g / m2.
2. More dense roofing - 350 g / m2.
The marking of the RPP stands for Lining Ruberoid. It is smooth. PKK is a roofing material. He is sprinkled. Personally, before me was a choice between RPP and RPP (o). The letter in parentheses means lite. It is used not only on concrete substrates, but also on roofs, where light weight is a priority. I chose without the letter O.
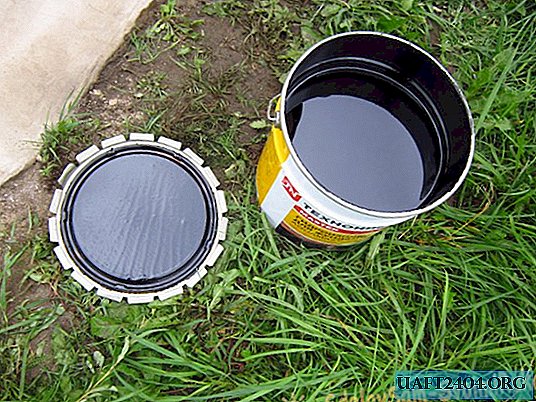
Among the bituminous mastics, I chose the cold version under the brand name Aquamast from Technonikol. The line of these mastics is intended for domestic use. Most likely, there are differences from the professional series. But I worked with this material for the first time. I will say this, I liked it:
- Mastic is easily spread on concrete.
- It has a good adhesive effect.
- Doesn’t have an unpleasant odor. Although all the work was carried out on the street.
Among the minuses, I highlight those with which I could not cope due to inexperience: - Mastic is very dirty. You need to be careful or wear protective clothing, which is not a pity.
- It dries for a long time. In the open sun, there is enough days, but under the ruberoid, the drying time is several days. It depends on air temperature and humidity.
- Does not tolerate contact with water. It was my deplorable experience. About him further.
Mastic consists of petroleum bitumen with a solvent. For more curious builders, I will list the technical characteristics of the product to cover the foundation:
- Adhesion Strength 0.1 MPa. This applies to concrete, metal, wood.
- Water absorption per day 2% by weight.
- Water resistance is positive. The conditions for time and pressure are 72 hours and 0.001 MPa, respectively.
- The share of non-volatile substances from 75 to 90%.
- Use temperature from -10 to +40.
- The layer dries a day. My observations confirm a longer drying time.

The materials I purchased were fresh, free of defects. This is the main question when choosing even expensive building material.
The technological process of waterproofing the strip foundation
Isolation by means of roofing material is divided into horizontal and vertical cutoff. From the name it is clear that vertical protection is attached to the inside of a wooden formwork. I will miss her description, because I did not. Although this is not a big deal:
- The required size of ruberoid flaps is measured.
- Stripes are cut taking into account overlaps.
- Fasten to a tree on a construction stapler.
Horizontal bonding of roofing material to the mastic is of great interest. To work, you need a construction tool.
Tools
- Rigid brush for cleaning concrete surfaces.
- Gloves.
- Metal spatula.
- Paint brush.
- Stick for mixing mastic.
- Knife for cutting roofing material.

Now comments. Since I was mistaken in something, having prepared the tools initially. A stiff bristle brush is definitely needed. Otherwise, you will have to sweep away the dust with your hand, grass, or something else. You can not do it this way. You can’t do without gloves either. But accuracy is important, since mastic is very smeared. I had low hopes for a metal spatula, and it turned out to be the main tool. The main thing is that the metal thickness is at least 1 mm. A prerequisite when working with cold bitumen was the second spatula to remove excess black stretching material from the first spatula.


I made a mistake with the brush and stained it in vain. The brush is not suitable for such work. And I had to throw my own. The stick was also not a good idea, since the mastic did not have to be stirred. As for the knife, I will say the following. An ordinary stationery knife cuts roofing material in one pass. Although there are more advanced models of blades with a curved tip. They are more convenient. I also used an improvised hard roller to press the material.

And also after an error related to weather conditions, he used a building hair dryer to heat and dry the concrete surface. And now I turn to small instructions for laying protection on the foundation. Let the short description move novice masters to their own trial and error.
Procedure
- Here you can not be mistaken in the size of segments of bitumen cardboard.
- It is necessary to correctly mark the overlaps.

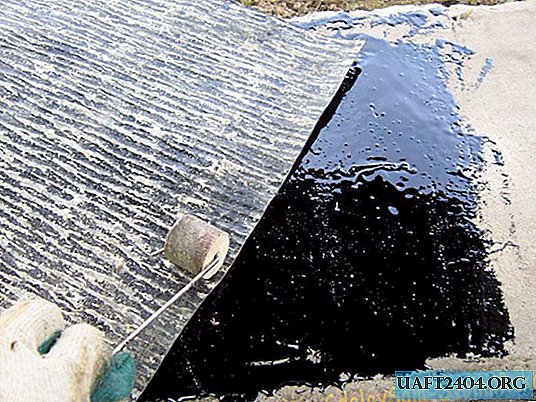
- After cutting all the shreds, proceed to applying the mastic.
- The mastic must be pry off with a trowel, periodically scrolling around the axis. This is a safety net against jumping off the material from the trowel.

Apply to concrete in several ways: - A lot of the distributed areas with further spreading.
- Little by little. But by doing this in sequence, creating a thin layer.

- Overdoing with a layer thickness is not necessary. Since the manufacturer himself warns that the layer does not dry out or leak at high air temperature.
- Next, the sheets are stacked one after another.

Now about the bugs.
Waterproofing Errors
It started to rain during operation. Part of the surface of the foundation with mastic applied. Bitumen just spread in the water. I did not expect this. That is, it stuck around the wet area. I corrected the situation by drying with a building hair dryer. But this is also not the best option. In case of such an error, work should be stopped until the concrete has dried naturally. But I decided to take a chance by drying the surface. Then, I glued a piece of roofing material. Dry the layer for a very long time. Fortunately, the month was hot. Among other minor errors, I highlight:
- Incorrect trimming of roofing material. I wanted to save, but it turned out the other way around.
- Disposal of the paint brush. She also cost money.
- Inaccuracy due to which the gloves got dirty.
But in all of the above, there is less trouble than neglecting the foundation waterproofing installation complex. It is impossible to achieve high-quality protection if you do not use underground insulation, as well as impregnation with spent fuel and lubricants. This I say based on personal experience.
Conclusion
A practical builder will have a reasonable question: is it permissible to produce a responsible section of waterproofing? For me, the answer is simple. Yes and no. In the first case, the reasons are as follows:
- This is my first experience without any help.
- The area of the house and the volume of concrete pouring are relatively small for significant cash costs.
- The load on the foundation is small.
- The water table is deep.
The second answer involves decades of waterproofing technology. It is being improved only in terms of new products among building materials. But using one horizontal layer does not protect completely. And the complex is a guarantee of long-term operation without problems.
Share
Pin
Tweet
Send
Share
Send